
The CDN acronym is becoming more popular among website administrators and developers in the vast world of technology, thanks to the numerous benefits it offers to websites and applications.
If you are unfamiliar with CDN or wish to learn more about it, join us in this article to discover how to utilize a CDN for your website.
Content Distribution Network
CDN stands for Content Delivery Network and its main aim is to distribute digital content over the internet through multiple data centers to enable faster access for users.
This feature was first utilized for storing and sharing multimedia content such as images, audios, and videos. In this approach, the hosting server stores the site’s logical components, while a CDN handles the heavier content like images and static files. This method continues to be commonly employed today.
The use of CDN has advanced to include storing full versions of websites and applications, along with their source code, offering various benefits that will be discussed in this article. But before that, let’s explore the functioning of this technology.

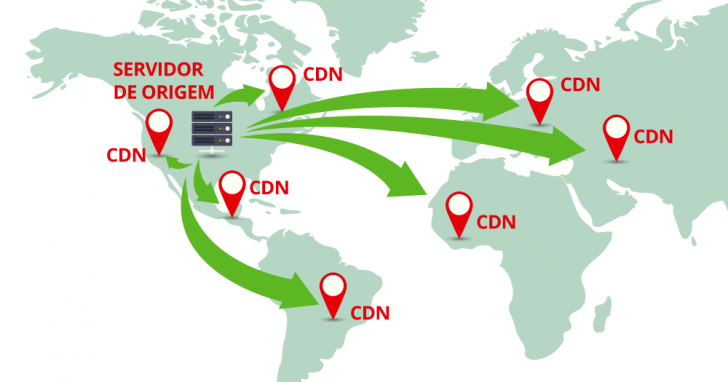
How does a Content Delivery Network operate?
The scenario involves buying a book online from a store in the United States, which will require shipping to Brazil and may take weeks to arrive.
If you purchase the book from the virtual store with a branch in Brazil, the book will be shipped to you from a local address, reducing the delivery time compared to when it would be sent from the United States.
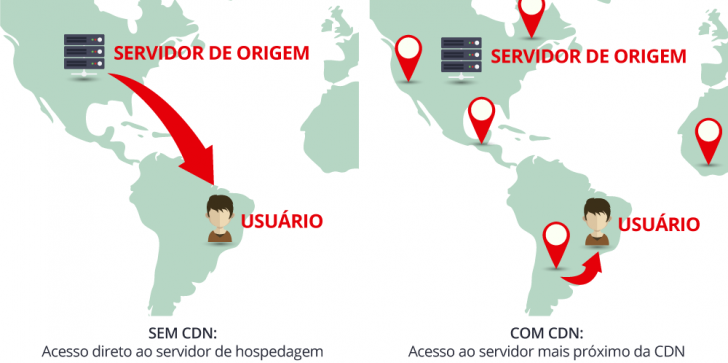
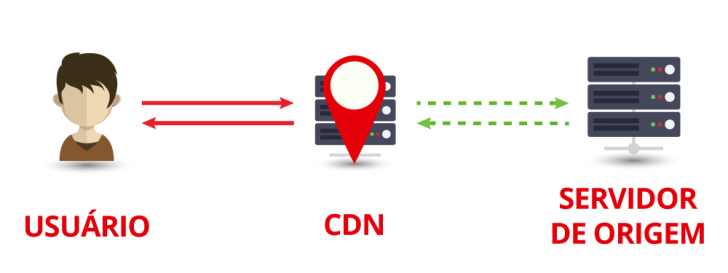
A content delivery network (CDN) operates in the digital realm of the internet, delivering website files from a server located nearer to the user than the original server.
When you visit a website connected to a CDN, the site’s content is fetched from the closest data center to your location. For instance, when you visit Amazon’s site, even though its main server is in the US, you will be served content from a server in Brazil.

Benefits of utilizing a content delivery network
Now that we have a grasp of the idea, let’s explore the practical benefits of utilizing a content distribution network.
- The server’s proximity to the user leads to faster server response times, resulting in quicker delivery of requested content, which can save a few seconds depending on the server’s location.
- The site experiences enhanced performance due to the static copies of site pages being sent, instead of dynamic content that would require processing by the source server for each request. Additionally, the majority of traffic is handled by the CDN, resulting in a significant decrease in the hosting server’s resource consumption compared to a site without this feature.

- A content delivery network (CDN) can manage high volumes of traffic effectively, surpassing the capacity of a shared hosting server. This makes it valuable for websites needing to cater to substantial traffic demands.
- A content delivery network provides various security measures to prevent and potentially block traffic from suspicious sources, including malicious bots and scripts that aim to compromise websites and steal sensitive information.
- Many hosting companies provide protection against DDoS attacks, but it is not yet a widespread feature. CDNs are equipped to handle and defend against such threats automatically.
Explore: Site Shielding – Keeping Your Website Safe from Online Dangers
Using a Content Delivery Network (CDN) on your website
It has two main uses: storing and serving static features, or functioning as a reverse proxy with a static copy of the entire site. Let’s delve deeper into how each method operates.
Providing solely unchanging material
A typical website includes elements like images, style sheets, and scripts that are not regularly updated. By utilizing a CDN, you can store and deliver this content to users when they visit your site. This helps the hosting server manage user requests while the CDN serves static content.
To gain better comprehension, think about the common loading process of a website, as shown below:
Normal website example:
If the website utilized a content delivery network (CDN) to store its static content, the process of uploading content would resemble the following illustration.
Site example that uses CDN:
To utilize this setup, you must establish a subdomain and link it to the content distribution network. Afterward, configure your website to fetch the static files from this updated URL.
In this situation, all traffic goes to your hosting server, but some content is delivered by a CDN, helping to lessen the server load. Another technique can further reduce the hosting server’s resource usage.
Storing an entire duplicate of the website
The CDN functions as a reverse proxy in this method, requiring the domain’s DNS to be directed to it so that all site traffic is routed to the content distribution network servers.
CDN saves a cached version of the entire website, sending the response to the user without contacting the hosting server if all necessary resources are in the cache. Requests for uncached features are sent to the original hosting server.

This situation is particularly intriguing for websites and blogs due to the static quality of their content.
How expensive is a CDN?
You may believe that such a feature would be expensive and beyond your budget, but you can actually access this technology for free without compromising on quality.
Some specialized companies provide free plans, offering basic CDN features to all users with advanced features available for separate purchase. These extras are optional, allowing anyone to benefit from a content distribution network service. CloudFlare and Incapsula are examples of companies offering free plans.
Another method to utilize this feature at no cost is by bundling it with a web hosting package. Providers such as HostGator and Hostinger include CloudFlare for free in their shared hosting plans.
Prices for a paid plan can vary significantly. Typically provided by international companies, these services are billed in dollars. In Brazil, GoCache offers plans starting at R$ 29.90 per month. International plans begin at $9 per month for MaxCDN and $20 per month for CloudFlare. The next tier above the free plan, offered by Incapsula, is priced at $59 per month.
Cloud hosting companies provide content distribution services as well. Amazon AWS and Google Cloud Platform are prominent players in this field, offering more intricate service configurations.
Conclusion
Choosing a Content Delivery Network (CDN) can be a wise and essential decision due to the benefits it offers. It is a good strategy to handle increased traffic and safeguard your website from harmful scripts and attacks.
Do you have any inquiries or recommendations? Feel free to leave a comment and start a conversation!
Publication date: 17/04/2017 (last modified on 13/09/2023)
CloudFlare and Concepts are relevant tags.
